Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS)
Optimizing laboratory data management involves improving how scientific, technical, or analytical data is collected, stored, processed, secured, and utilized. The goal is to make processes more efficient, reliable, and traceable.
A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a hybrid system—comprising both infrastructure and software—specifically designed to manage, organize, process, store, and secure laboratory data.
This system ensures:
1. Sample Management
-
- Sample Tracking: It allows laboratories to record, identify, and track samples throughout their lifecycle, from receipt to analysis and archiving.
- Traceability: Moreover, each sample is linked to a unique identifier (e.g., barcode, QR code), ensuring full traceability.
- Organization: Additionally, it facilitates classification and quick access to all relevant information.
2. Process Automation
-
- Communication with Instruments: The system automatically collects results from analytical devices, thereby eliminating manual entry.
- Standardization: Furthermore, it enforces strict protocols, ensuring that all analyses follow the same structured steps.
- Automatic Notifications: In addition, it sends alerts for critical events, such as analysis delays or anomalies.
3. Productivity Improvement
-
- Error Reduction: By automating processes and centralizing data, the system significantly reduces human errors.
- Resource Optimization: It also enables efficient planning of equipment, reagents, and personnel.
- Process Acceleration: Consequently, it streamlines various laboratory steps, reducing the time required to deliver results.
4. Data and Results Management
-
- Data Centralization: All information is stored in a single, secure, and easily accessible database.
- Data Analytics: Additionally, it provides in-depth visualizations, reports, and analysis tools.
- Archiving: Finally, it ensures long-term storage of data for future reference or audit purposes.
5. Regulatory Compliance
-
- Standards Compliance: The system helps laboratories comply with international standards such as ISO 15189, ISO 17025, and other regulatory requirements.
- Complete History: Moreover, it provides a detailed audit trail, ensuring all laboratory activities are recorded and verifiable.
- Document Management: It also keeps protocols, procedures, and reports updated and compliant at all times.
6. Security and Traceability
-
- Controlled Access: Laboratories can manage user rights, ensuring only authorized personnel access sensitive data.
- Change History: Furthermore, every system modification is logged and traceable, guaranteeing full accountability.
7. Planning and Logistics
-
- Inventory Tracking: The system helps manage consumables and product stocks, preventing shortages and waste.
- Task Planning: In addition, it organizes analyses, staff assignments, and equipment schedules efficiently.
8. Improved Collaboration
-
- Data Sharing: Results can be quickly shared between teams, departments, or even across different laboratories.
- Multi-Site Management: Lastly, the system supports operations across multiple laboratories, enabling centralized control from a single platform.
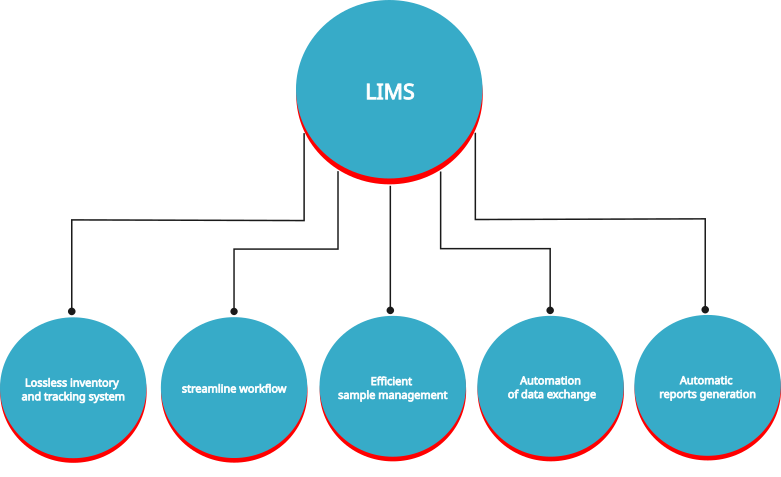
Benefits of LIMS
Main functions of LIMS
Order Registration
-
- The first step involves establishing a test contract between the client and the laboratory, defining the scope and requirements of the tests.
Reception of Samples
-
- Upon arrival, samples are carefully monitored and registered.
- Additionally, detailed information, such as photos, origin, type, and condition, is recorded on a life sheet.
- If any issues arise, the physical and logical conditions (for electronic samples) are verified, allowing for the fastest possible return if necessary.
- Furthermore, each sample is automatically identified and assigned a unique identifier (barcode or QR code).
Preparation of Samples for Testing
-
- Next, test information is automatically added to the life sheet in accordance with the contract terms.
- The samples are then temporarily stored in the exchange area, awaiting further processing.
Task Allocation
-
- The life sheets are distributed efficiently to the relevant stakeholders to ensure smooth workflow management.
Test Planning
-
- Tests are scheduled systematically, ensuring optimal organization and resource utilization.
Sample Testing
-
- Before each test, a systematic check of the test equipment and environmental conditions is conducted to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Data Recording
-
- Once the tests are completed, data is automatically retrieved through a direct connection to databases via API, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
Results Control
-
- To guarantee accuracy, results undergo strict quality control in compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 17025 and ISO 15189.
Preparation of Test Reports and Certificates
-
- Reports and certificates are automatically generated, reducing manual work and minimizing human errors.
Control of Reports and Certificates
-
- In addition, the conformity of reports and/or certificates is carefully monitored to ensure adherence to quality standards and regulatory requirements.
Provision of Results to the Customer, Invoicing, and Archiving
-
- Finally, results and invoicing files are automatically sent to the customer.
- At the same time, samples and life sheets are securely archived for future reference.